Blisterata is a term that may seem unfamiliar to many, but it encompasses a fascinating and significant concept in various fields. This comprehensive guide aims to delve deep into the world of blisterata, exploring its definitions, applications, and implications across different disciplines. From biological phenomena to technological advancements, we will uncover the myriad ways in which blisterata influences our understanding and experience of the world.
What is Blisterata?
Defining Blisterata
The term “blisterata” originates from the Latin word “blister,” meaning a small bubble on the skin filled with serum and caused by friction, burning, or other damage. In a broader context, blisterata refers to any small, bubble-like formation or occurrence, not limited to biological contexts. This concept extends into various fields, from natural sciences to engineering and technology.
Historical Context
The study of it has historical roots in medicine and biology, where understanding the formation and treatment of blisters was crucial. Over time, the concept expanded, finding relevance in materials science, geology, and even aerospace engineering. This historical evolution showcases the interdisciplinary nature of blisterata and its importance across different areas of study.
Biological Significance of Blisterata
Blister Formation in Humans
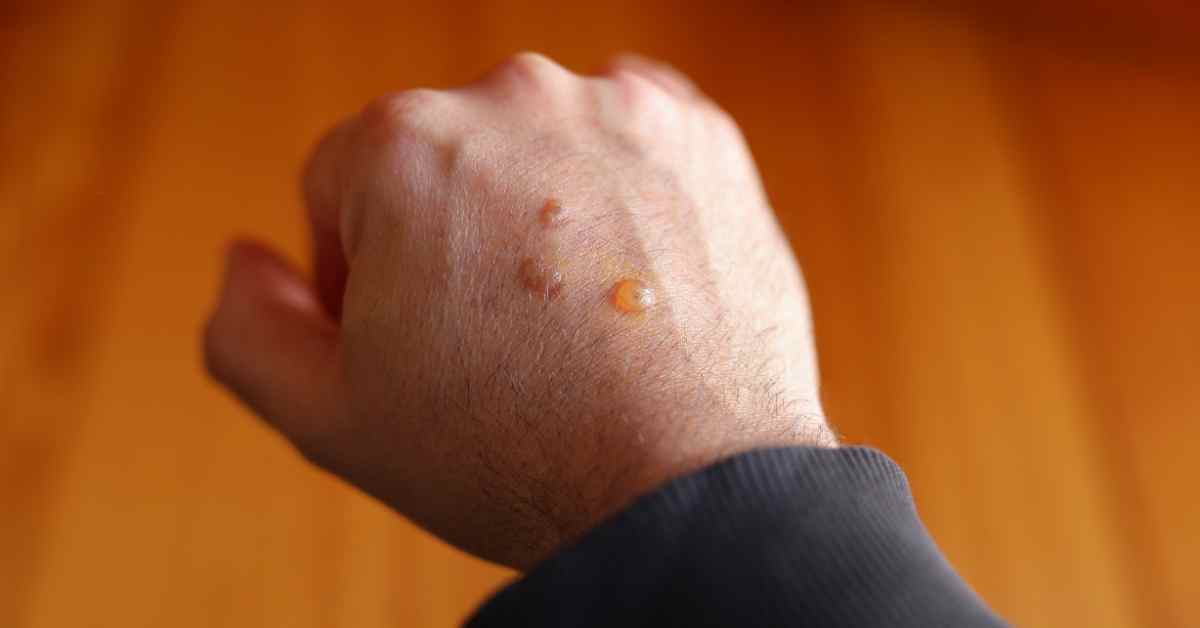
Blisters are a common occurrence in human biology, often resulting from friction, burns, or underlying medical conditions. These fluid-filled sacs serve as the body’s protective mechanism, cushioning damaged tissue and promoting healing.
Causes of Blisters
- Friction Blisters: Caused by repetitive rubbing, often on hands or feet.
- Burn Blisters: Result from thermal, chemical, or electrical burns.
- Blisters from Medical Conditions: Conditions like chickenpox, herpes, and eczema can cause blister formation.
Treatment and Care
Proper care of blisters involves:
- Keeping the area clean and dry.
- Using protective dressings to prevent infection.
- Avoiding the deliberate popping of blisters to reduce infection risk.
Blisterata in Plant Biology
Plants also exhibit it, commonly referred to as galls or blisters. These formations occur due to various factors, including insect activity, fungal infections, and environmental stress.
Causes and Implications
- Insect Activity: Certain insects lay eggs on plants, causing tissue swelling and blister formation.
- Fungal Infections: Fungal spores can invade plant tissue, leading to blister-like symptoms.
- Environmental Stress: Extreme weather conditions can cause blisters on plant leaves and stems.
Understanding these formations is crucial for managing plant health and preventing crop loss in agriculture.
Blisterata in Materials Science
Blister Formation in Metals and Polymers
In materials science, it refers to the formation of small, bubble-like defects within metals and polymers. These defects can significantly impact the material’s integrity and performance.
Causes of Blister Formation
- Manufacturing Defects: Imperfections during the manufacturing process can lead to blister formation.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, and chemical agents can cause blisters in materials.
- Mechanical Stress: Repeated stress and strain can create internal bubbles within materials.
Implications for Material Performance
Blisters in materials can weaken structural integrity, leading to potential failures in critical applications. For example:
- Aerospace Industry: Blisters in aircraft components can compromise safety and performance.
- Automotive Industry: Blisters in car parts can affect durability and reliability.
Understanding and mitigating it in materials is essential for ensuring safety and longevity in various industries.
Geological Blisterata
Volcanic Blisters and Lava Blisters
In geology, it can refer to volcanic and lava blisters, which are bubble-like formations created during volcanic activity.
Volcanic Blisters
- Formation: Volcanic blisters form when trapped gases within molten rock create pressure, leading to bubble-like protrusions on the surface.
- Significance: These formations provide valuable insights into volcanic processes and the behavior of magma.
Lava Blisters
- Formation: Lava blisters occur when lava flows over uneven terrain, trapping gas pockets that create bubble-like structures.
- Significance: Studying lava blisters helps geologists understand the dynamics of lava flow and cooling processes.
Blisterata in Sedimentary Rocks
Blister-like formations can also occur in sedimentary rocks, often due to the release of trapped gases during sediment compaction.
Causes and Implications
- Gas Release: As sediments compact and solidify, trapped gases can escape, creating small cavities or blisters.
- Geological Insights: These formations provide clues about the conditions and processes involved in sedimentary rock formation.
Technological Applications of Blisterata
Blisterata in Electronics
In electronics, it can refer to the formation of bubbles or voids within semiconductor materials, impacting device performance.
Causes of Blister Formation
- Manufacturing Defects: Imperfections during semiconductor fabrication can lead to blister formation.
- Thermal Stress: Exposure to high temperatures during device operation can create internal bubbles.
Mitigating Blisterata in Electronics
- Improved Manufacturing Processes: Enhancing fabrication techniques to reduce defects.
- Thermal Management: Implementing effective cooling solutions to minimize thermal stress.
Blisterata in Coatings and Paints
Blistering in coatings and paints is a common issue that affects the aesthetic and protective properties of surfaces.
Causes of Blister Formation
- Moisture Trapping: Trapped moisture between layers can cause blisters as it evaporates.
- Improper Surface Preparation: Inadequate cleaning and priming can lead to blistering.
Preventing and Repairing Blisterata in Coatings
- Proper Surface Preparation: Ensuring surfaces are clean and primed before applying coatings.
- Quality Materials: Using high-quality paints and coatings to reduce blistering risk.
- Regular Maintenance: Inspecting and repairing blisters promptly to prevent further damage.
Future Directions and Research
Advancements in Blisterata Research
Ongoing research aims to deepen our understanding of blisterata across various fields. Key areas of focus include:
- Biological Research: Investigating the genetic and molecular mechanisms behind blister formation in humans and plants.
- Materials Science: Developing new materials and manufacturing techniques to prevent blistering.
- Geological Studies: Enhancing our knowledge of volcanic and sedimentary processes through the study of blister formations.
- Technological Innovations: Improving electronic device performance by addressing blisterata in semiconductors.
Potential Applications
- Medical Treatments: Developing advanced treatments for blister-related conditions in humans.
- Agricultural Practices: Enhancing crop protection by understanding and preventing plant blisters.
- Industrial Applications: Creating more durable materials and coatings to prevent blistering in various industries.
Conclusion
Blisterata, a term that encompasses various bubble-like formations across multiple disciplines, is a fascinating and multifaceted concept. From biological phenomena to technological advancements, understanding blisterata is crucial for improving health, enhancing materials, and advancing scientific knowledge.
In biology, blisters play a vital role in protecting and healing damaged tissue in humans and plants. In materials science, preventing blister formation is essential for maintaining the integrity and performance of metals and polymers. Geologically, studying blister formations provides valuable insights into volcanic and sedimentary processes. In technology, addressing it in electronics and coatings ensures the reliability and longevity of devices and surfaces.
As research continues to unravel the complexities of blisterata, its significance across various fields will undoubtedly grow. By deepening our understanding and developing innovative solutions, we can mitigate the challenges associated with blisterata and harness its potential for positive applications.
This comprehensive guide to blisterata underscores the importance of interdisciplinary research and collaboration in addressing this intriguing phenomenon. Whether in the natural world or the realm of technology, blisterata remains a key area of study with far-reaching implications.
Read More: Andrew Santino Wife: An In-Depth Look at the Personal Life of the Comedian